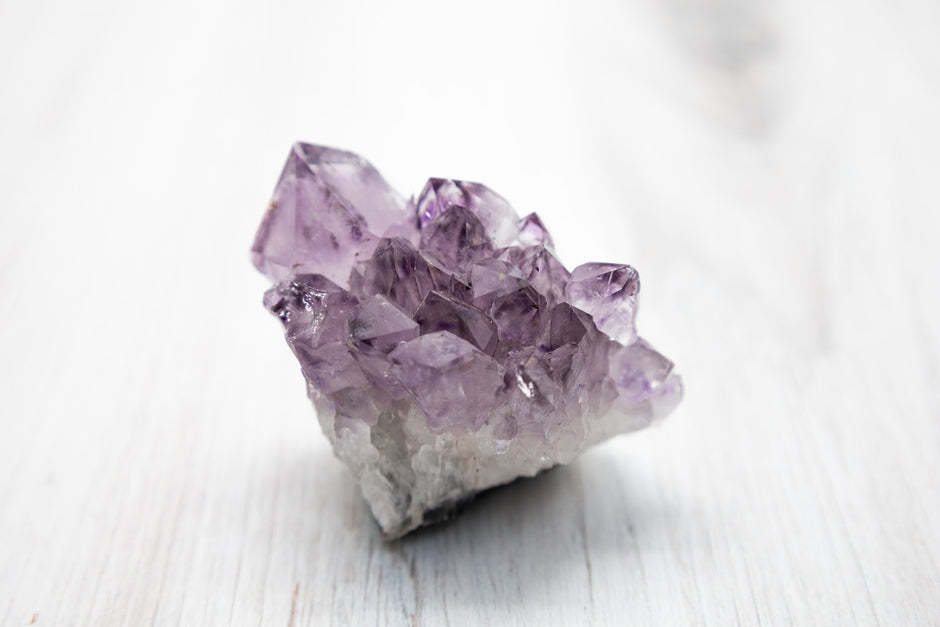
Welcome to an exploration of "Gemstone Mines and Their Historical Significance," a topic that delves deep into the earth—quite literally—to unearth the fascinating history of gemstone mining. Gemstones have captivated human imagination for centuries, not just for their dazzling beauty but also for their rarity and the intricate methods involved in extracting them from the earth. This article aims to shed light on the historical significance of gemstone mines, tracing the evolution of mining techniques from ancient times to the present day. Whether you're a history buff, a gemstone enthusiast, or someone who appreciates the blend of nature's artistry and human ingenuity, this comprehensive guide offers a wealth of information that promises to enrich your understanding of this captivating subject.
Stay tuned as we delve into the ancient art of gemstone mining, explore the technological advancements that have revolutionized this industry, and examine the ethical considerations that come with extracting these beautiful stones from the earth.
The Allure of Gemstones
Gemstones have long been objects of desire, capturing the human imagination with their stunning beauty, vibrant colors, and unique characteristics. From the deep blue sapphires that have adorned royal crowns to the dazzling diamonds that symbolize eternal love, gemstones hold a special place in our lives and cultures. But what is it that makes these stones so alluring?
Rarity and Value
One of the key factors that contribute to the allure of gemstones is their rarity. Unlike common rocks, gemstones are mineral formations that occur under specific natural conditions, such as pressure and temperature. This rarity of a gemstone often translates into high value, making gemstones a lucrative commodity in various markets around the world.
Symbolism and Cultural Significance
Gemstones are not just beautiful to look at; they often carry deep symbolic meanings. For instance, emeralds have been associated with fertility and rebirth, while rubies symbolize passion and courage. These cultural associations add another layer of allure to these already captivating stones.
Versatility and Utility
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, gemstones have practical applications as well. They are used in various industries, including electronics, healthcare, and even space exploration. For example, diamonds are not just a girl's best friend; they are also used in cutting and drilling due to their hardness.
Emotional Connection
Many people feel a deep emotional connection to gemstones, whether it's a birthstone or a stone that holds sentimental value. This emotional aspect often makes gemstones treasured family heirlooms, passed down from generation to generation.
The Role in Jewelry and Fashion
It's impossible to discuss the allure of gemstones without mentioning their role in jewelry and fashion. From simple rings to elaborate necklaces, gemstones have been used to create pieces of art that we wear, further enhancing their allure and prestige.
The Ancient Art of Gemstone Mining
The quest for gemstones is as old as civilization itself, a testament to the enduring allure these natural wonders have held for humanity. But have you ever stopped to wonder how the ancient people, devoid of modern technology, were able to extract these precious stones from the earth? The ancient art of gemstone mining is a fascinating journey through time, revealing the ingenuity and determination of our ancestors.
In ancient times, gemstone mining was a far less complex endeavor than it is today. Early humans would often find gemstones like citrine, amethyst, and even diamonds in riverbeds, where natural erosion had exposed these treasures. Surface mining was another common method, where gemstones found close to the earth's surface were easily extracted using basic tools like picks and shovels.
One of the earliest known gemstone mines is the lapis lazuli mines in Afghanistan, which dates back to as early as 7,000 BCE. This vivid blue stone was highly prized in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. Similarly, diamonds were being mined in India around 3,000 BCE, and their value was well recognized in ancient civilizations.
The tools used in ancient gemstone mining were rudimentary compared to today's standards. Picks made from antlers or bones and simple chisels were the primary tools of the trade. Despite the lack of advanced tools, ancient miners demonstrated remarkable skill in locating and extracting gemstones. They employed techniques like tunneling and open-pit mining, albeit on a much smaller scale than we see today.
In the Middle Ages, gemstone mines often came under the control of royalty or nobility. The ownership of a productive mine was a significant asset, contributing to the wealth and prestige of ruling families. This led to more organized and systematic mining operations, including the use of slave or serf labor in some instances.
In many ancient cultures, gemstones were believed to possess magical or spiritual properties. Mines were often shrouded in mystery and folklore, with rituals and prayers conducted to appease the 'spirits' of the mine. These beliefs added an extra layer of significance to the act of mining, making it not just a physical but also a spiritual endeavor.
The gemstones extracted from these ancient mines were not just pretty ornaments; they were valuable trade commodities. The trade of gemstones along routes like the Silk Road had a significant economic impact, contributing to the prosperity of ancient civilizations.
In essence, the ancient art of gemstone mining is a captivating tale of human ingenuity, perseverance, and the eternal quest for beauty and wealth. While the methods have evolved, the allure and significance of gemstone mines remain as potent as ever, linking us back to a time when the earth's hidden treasures were just beginning to reveal themselves to humanity.
Evolution of Gemstone Mining Techniques
The art of extracting gemstones from the earth has come a long way since the days of rudimentary picks and shovels. As our understanding of geology advanced and technology evolved, so did the techniques used in gemstone mining. This section delves into the fascinating evolution of gemstone mining techniques, tracing the journey from ancient practices to the sophisticated methods employed today.
The Middle Ages: The Dawn of Systematic Mining
By the time the Middle Ages rolled around, gemstone mining had become a more organized and systematic affair. Techniques like tunneling became more refined, and open-pit mining was employed to reach gemstones located deeper within the earth. The use of water wheels and rudimentary pulley systems also made the extraction process more efficient.
The Renaissance: Technological Advancements
The Renaissance period saw significant advancements in mining technology. Innovations like the Archimedean screw and more advanced pulley systems allowed for deeper and more efficient mining. The period also saw the introduction of new tools made from iron and steel, which greatly enhanced the miners' capabilities.
The Industrial Revolution: A Paradigm Shift
The Industrial Revolution was a game-changer for gemstone mining. The advent of steam power and later, electricity, revolutionized the industry. Heavy machinery like drills and hydraulic systems made it possible to mine at depths previously unimaginable. This period also saw the introduction of blasting techniques, using gunpowder to break through hard rock.
Modern Times: Precision and Sustainability
Today, gemstone mining is a highly sophisticated operation that employs advanced technologies like underground mining, hydraulic mining, and even laser cutting for gem extraction. Computer-aided design (CAD) software is used for mapping and planning, ensuring that the mining is as precise as possible. Moreover, there's a growing emphasis on sustainable mining practices to minimize environmental impact.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
As technology has advanced so has our understanding of the ethical and environmental implications of mining. Modern mining operations often employ sustainable practices, such as land reclamation and water treatment facilities, to minimize their ecological footprint. Ethical sourcing of gemstones has also become a significant focus, ensuring that the gems are conflict-free and that the mining practices adhere to international labor laws.
The Future: Towards More Sustainable Practices
Looking ahead, the focus is on making gemstone mining more sustainable and less invasive. Technologies like remote sensing and satellite imagery are being used to locate gemstone deposits without disrupting the ecosystem. Research is also underway to develop more eco-friendly extraction methods.
How Mining Affects Gemstone Quality
When it comes to gemstones, quality is often the first thing that comes to mind. From the brilliant sparkle of a diamond to the deep hues of a sapphire, the quality of a gemstone can significantly influence its value and allure. But did you know that the mining process itself plays a crucial role in determining the quality of these natural treasures? Let's delve into how different mining techniques can impact the quality of gemstones.
1. The Role of Natural Elements
Before discussing mining, it's essential to understand that gemstones are formed under specific natural conditions involving elements like water, pressure, and heat. These conditions can vary from one geological setting to another, affecting the quality of the gemstones found there. For example, the presence of certain minerals in the earth can enhance the color of a gemstone, making it more valuable.
2. Traditional vs. Modern Mining Techniques
Traditional mining techniques, such as tunneling and open-pit mining, often involve a greater degree of manual labor and less precision. While these methods have been effective for centuries, they can sometimes lead to the inadvertent damage of gemstones during extraction. Modern techniques like hydraulic mining and laser cutting offer more precision, reducing the risk of damaging the gemstones and thereby preserving their quality.
3. The Impact of Blasting
Blasting is a common technique used in gemstone mining, especially for extracting stones from hard rock formations. While effective, blasting can sometimes cause fractures or inclusions in the gemstones, reducing their overall quality. Therefore, this technique is generally avoided for more delicate or high-value stones.
4. Ethical and Sustainable Mining
Ethical mining practices not only focus on human and environmental welfare but also on the quality of the gemstones. Sustainable mining methods aim to minimize waste and damage, ensuring that the gemstones are extracted in their most natural and pristine form.
5. Quality Control Measures
In modern gemstone mining operations, quality control measures are often in place to ensure the highest quality yield. These may include initial assessments to determine the quality of the gemstone deposit, careful planning of the mining operation, and even on-site gemologists to assess the quality of the gemstones as they are extracted.
6. Post-Extraction Treatment
It's worth noting that some gemstones undergo treatments after extraction to enhance their quality. While this is common practice, it's essential to disclose any treatments as they can affect the gemstone's value and longevity.
In summary, the mining process plays a significant role in determining the quality of gemstones. From the techniques employed to the ethical considerations, various factors can influence the final quality of these natural wonders. As technology and ethical practices continue to evolve, the focus remains on extracting gemstones in a manner that preserves their innate beauty and value, ensuring that these natural treasures continue to captivate us for generations to come.
In Conclusion
From the ancient art of gemstone mining to the cutting-edge techniques of today, the journey of extracting these natural wonders from the earth is as fascinating as the stones themselves.
We've explored the allure that has made gemstones objects of desire across cultures and eras, delved into the historical significance of gemstone mines, and examined how mining techniques have evolved to become more efficient and ethical. We've also looked at the critical aspect of how these mining methods impact the quality of the gemstones, a factor that significantly influences their value and allure.
As we've seen, gemstone mining is not just a commercial endeavor but a blend of history, science, and even spirituality. It's a field that has seen remarkable advancements, yet holds true to its ancient roots, reflecting the enduring human fascination with the beauty and mystery of the natural world.
As we continue to seek these beautiful stones, whether for their aesthetic, emotional, or financial value, it's essential to remember the complex journey they undergo—from deep within the earth to the sparkle in a piece of jewelry. Here's to the fascinating world of gemstones and the intricate art and science of bringing them to light!